File Server Vs NAS

Considering whether to use a file server vs NAS (Network Attached Storage) for your data management needs? In this article, I’ll delve into the key differences between these two storage solutions to help you make an informed decision.
When it comes to storing and accessing files in a networked environment, understanding the distinct functionalities of a file server vs NAS is crucial. I’ll break down the essential features of each option, highlighting their strengths and best use cases.
Whether you’re a small business looking to streamline data access or a home user wanting to centralize your media files, knowing the nuances of file servers and NAS devices can significantly impact your storage strategy. Let’s explore the nuances of file server vs NAS to determine which solution aligns best with your specific requirements.
Understanding File Servers
Definition and Basics
A file server is a specialized computer designed to store and manage files that can be accessed by other devices connected to the same network. It acts as a centralized location for data storage and sharing among multiple users.
File servers typically run on server operating systems and are equipped with high-capacity storage drives to accommodate large volumes of data. They enable efficient data management, access control, and data security within an organization.
Common Uses of File Servers
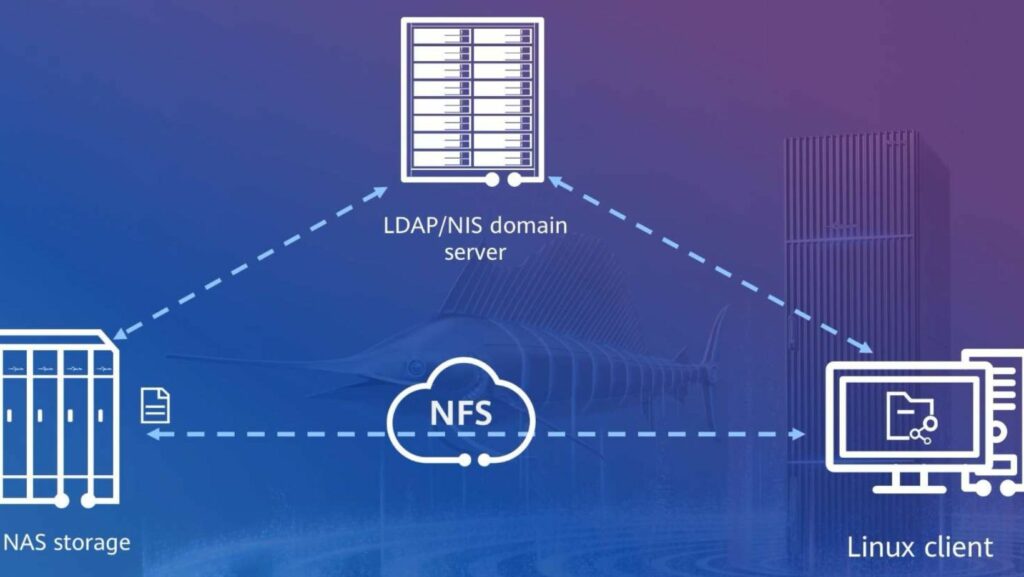
File servers serve various purposes across different types of environments. In businesses, they are commonly used to store and share documents, files, and applications among employees, promoting collaboration and seamless workflow. Educational institutions utilize file servers to manage student records, course materials, and research data securely. Additionally, file servers are employed in multimedia environments to store and distribute media files such as videos, music, and images efficiently.
These servers play a crucial role in facilitating data backup and recovery processes, ensuring data integrity and reliability. Moreover, file servers are instrumental in maintaining data consistency and preventing data duplication by providing a single source of truth for shared files. Their robust infrastructure and centralized management capabilities make them indispensable for organizations of all sizes looking to streamline data access and enhance data security practices.
Exploring NAS (Network Attached Storage)
NAS Fundamentals
NAS, or Network Attached Storage, is a specialized file storage device connected to a network, allowing multiple users to access data simultaneously. Unlike file servers, NAS systems are dedicated appliances optimized for file storage and retrieval, offering a cost-effective solution for data management.
Advantages of NAS Over Traditional Storage Methods
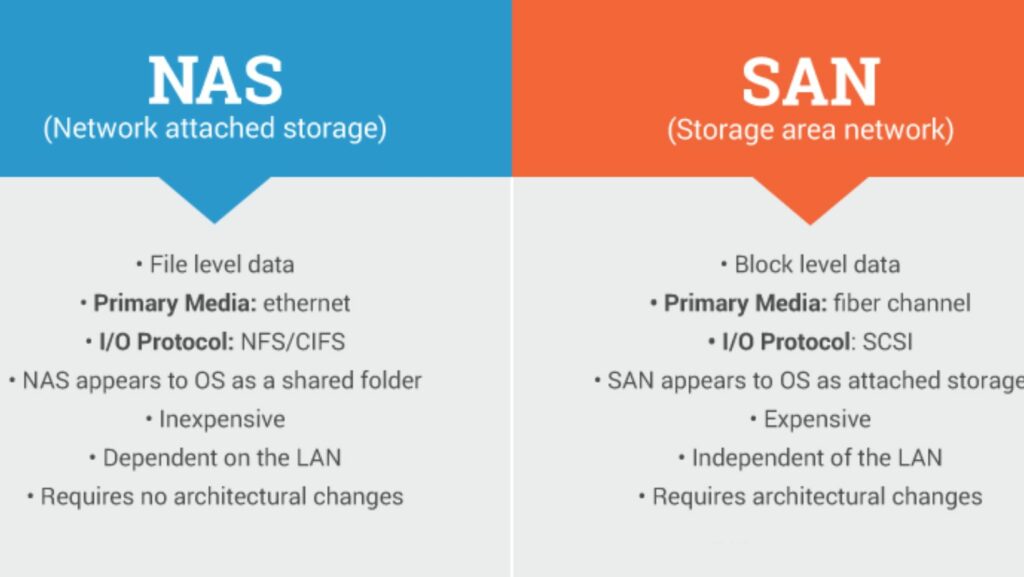
NAS provides several advantages over traditional storage methods like file servers. Firstly, NAS devices are easy to set up and manage, making them ideal for small businesses and home environments. Additionally, NAS offers scalability, allowing users to expand storage capacity seamlessly as data needs grow.
Secondly, NAS ensures efficient data access and backup processes, enhancing data retrieval speed and reliability. With built-in redundancy features like RAID configurations, NAS systems offer data protection against hardware failures, ensuring data integrity and availability.
Furthermore, NAS devices are energy efficient and compact, consuming less power and space compared to traditional file server setups. This makes NAS a suitable option for businesses looking to reduce operational costs and optimize physical space utilization.
NAS presents a compelling alternative to traditional file servers, offering ease of use, scalability, data protection, and cost efficiency for diverse data management requirements.
Performance Comparison
When it comes to performance, file servers and NAS devices operate differently. With a file server, data requests are processed using the server’s resources, which can potentially lead to slower performance during peak usage times. On the other hand, a NAS device is designed specifically for file storage and retrieval, offering optimized performance for data access tasks. This specialization often results in quicker response times and enhanced data transfer speeds compared to traditional file servers.
Cost Implications
In terms of cost, file servers and NAS devices have distinct financial considerations. File servers typically require dedicated hardware, including server machines, storage arrays, and networking equipment, which can incur higher upfront costs.